 What you eat (and how often you eat it) is a major factor in the ongoing battle to prevent tooth decay.
High levels of sugar or similar carbohydrates in your diet could encourage the growth of bacteria that cause tooth decay. Constantly sipping on acidic beverages like sodas or sports drinks can lead to enamel erosion.
What you eat (and how often you eat it) is a major factor in the ongoing battle to prevent tooth decay.
High levels of sugar or similar carbohydrates in your diet could encourage the growth of bacteria that cause tooth decay. Constantly sipping on acidic beverages like sodas or sports drinks can lead to enamel erosion.
You may be well aware of the kinds of foods that contribute to tooth decay. But did you know some foods can actually protect us from this damaging disease? Here are 4 kinds of foods believed to inhibit tooth decay.
Cheese. This food formed from milk is rich in calcium and has a stimulating effect on saliva. By eating a little cheese after a sugary snack, the increase in saliva can help neutralize the acid produced by the bacteria feeding on the sugar; the added calcium will also strengthen tooth enamel.
Fibrous plant foods. Beans, peanuts and leafy vegetables are rich in fiber and many require vigorous chewing. This in turn stimulates saliva flow, which as previously noted helps to neutralize high levels of acid.
Black and green teas. Beverages brewed from these plants are rich in polyphenols and flavonoids, providing an antioxidant effect on cells. Black tea also contains fluoride, which helps strengthen tooth enamel.
Chocolate. There’s some evidence that cocoa (from which chocolate is derived) may have some properties that inhibit tooth decay. But there is a catch — this evidence is based on unrefined cocoa, without the addition of any sugar. The high levels of sugar in processed chocolate negate this effect. Sorry chocolate lovers!
Of course, any of these and similar foods (like cow’s milk) should be considered complements to a comprehensive prevention approach that includes daily oral hygiene, limits on sugar and acidic food consumption and regular dental cleanings and checkups.
If you would like more information on preventing tooth decay, please contact Dr. Cindy Sumarauw at 801-281-3500 to schedule an appointment for a consultation. You can also learn more about this topic by reading the Dear Doctor magazine article “Nutrition & Oral Health.”

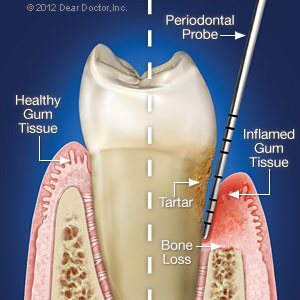 When we refer to periodontal (gum) disease, we’re actually talking about a family of progressive, infectious diseases that attack the gums and other tissues attached to the teeth. Caused primarily by bacterial plaque left on tooth surfaces from inefficient oral hygiene, gum disease can ultimately lead to tooth loss.
When we refer to periodontal (gum) disease, we’re actually talking about a family of progressive, infectious diseases that attack the gums and other tissues attached to the teeth. Caused primarily by bacterial plaque left on tooth surfaces from inefficient oral hygiene, gum disease can ultimately lead to tooth loss.